Datatypes Conversion in C#
- Implicit conversions
- Explicit conversions
- Difference between Parse() and TryParse()
Implicit conversion
Implicit conversion is done by the compiler
- when there is no loss of information if the conversion is done
- If there is no possibility of throwing exceptions during the conversion
Example: Write a program to convert integer to float with the use of variables.
In this case no loss of information, hence no need of explicit conversion.
using System; class Program { static void Main() { int a = 10; float f = a; Console.WriteLine(f); //Output will be 10 } }
Explicit Conversion
When there is data loss situation in conversion, we need to convert that data explicitly. See below example.
Example: Write a program to convert float to integer with the use of variables.
using System; class Program { static void Main() { float f = 123.45F; int i = (int)f; //using cast() operator int j = Convert.ToInt32(f); //using Convert class Console.WriteLine(i); //Output will be 123 Console.WriteLine(j); //Output will be 123 } }
Difference between Parse() and TryParse()
Use of Parse() method:
Write a program to save 100 as a string in string variable. Assign string variable value to the integer variable using parse methodusing System; class Program { static void Main() { string strNumber = "100"; int i = int.Parse(strNumber); Console.WriteLine(i); //output will be 100 } }
Use of TryParse() method:
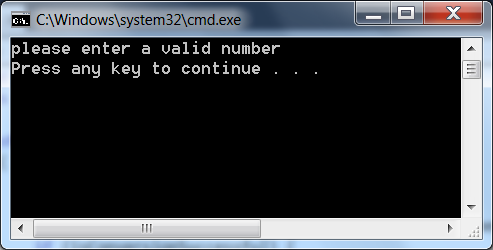
When your string contains non-numeric characters and try to assign that string value to interger, you will get complier error. To avoid the exception, we can make use of TryParse() method as below:
using System; class Program { static void Main() { string strNumber = "100ABC"; int result = 0; bool isConversionSuccessful = int.TryParse(strNumber, out result); if (isConversionSuccessful) { Console.WriteLine(result); } else { Console.WriteLine("please enter a valid number"); } } }


Comments
Post a Comment